
| China University of Petroleum | |||
| Chinese | |||
 |
|
||||||
Recently, Academician Sun Jinsheng's team at our institute has made new advances in the field of cellulose nanomaterials research. Their related work, Cellulose nanomaterials in oil and gas industry: Current status and future perspectives, has been published in the prestigious international journal Progress in Materials Science. The first author of the paper is Professor Li Meichun, with Academician Sun Jinsheng as the corresponding author. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation's Basic Science Center Project and other funding sources.

The related findings were published in Progress in Materials Science
Currently, China's oil and gas industry is in a critical transition period towards green and low-carbon development. In 2021, 17 petroleum and chemical enterprises, parks, and the Petrochemical Industry Association jointly signed and released the Declaration on Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality in China's Petroleum and Chemical Industry, integrating green and low-carbon development into the strategic planning of oil and gas enterprises. This closely links environmental protection principles with petroleum actions to ensure national energy security. To achieve green, low-carbon, and high-quality development in the oil and gas industry, environmental-friendly renewable materials and green technological innovations will play crucial roles.
Cellulose is the most abundant natural polymer material on Earth, with plants producing trillions of tons of cellulose annually through photosynthesis, making it an endlessly renewable resource. By methods such as mechanical shearing, chemical oxidation, enzymatic hydrolysis, and strong acid hydrolysis, natural plant fibers can be separated and broken down into ultrafine fibers with diameters smaller than 100 nanometers, known as cellulose nanomaterials. Cellulose nanomaterials possess a high aspect ratio, high surface area, controllable microstructure, surface chemical characteristics, excellent mechanical properties, gas barrier properties, thermal performance, and rheological properties. In recent years, they have sparked significant interest in the petroleum and natural gas industries.
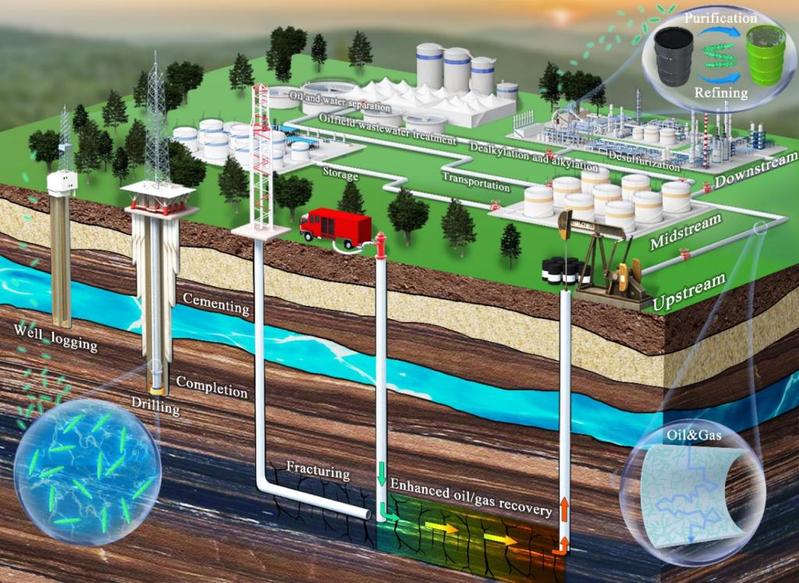
The application scenarios of cellulose nanomaterials in the oil and gas industry
The paper Research Status and Prospects of Cellulose Nanomaterials in the Oil and Gas Industry introduces the classification, preparation methods, and properties of cellulose nanomaterials. It points out that the raw materials and preparation methods of cellulose nanomaterials significantly impact their microstructure, surface functional groups, crystallinity, elastic modulus, thermal degradation performance, and rheological properties. Therefore, it is necessary to select the raw materials for cellulose nanomaterials carefully and regulate the preparation processes to meet the diverse demands of different application areas in the oil and gas industry. The paper summarizes the latest research progress of cellulose nanomaterials in upstream exploration and development, midstream transportation and storage, and downstream processing and refining fields.In the field of oil and gas exploration and development, cellulose nanomaterials can serve as rheology modifiers, fluid loss control agents, shale inhibitors, hydration enhancers, wetting agents, etc., in drilling fluids, cementing fluids, completion fluids, fracturing fluids, oil displacement fluids, promoting green, safe, and efficient exploration and development of oil and gas resources. In the field of oil and gas transportation and storage, cellulose nanomaterials can enhance the mechanical strength and gas barrier properties of oil and gas transmission pipelines and storage tanks, ensuring the safe and efficient transportation and storage of oil and gas resources. In the field of oil and gas processing and refining, cellulose nanomaterials can be used as templates for hydrophobic and functional modifications, providing excellent functions such as oil-water separation, desulfurization, and oil and gas cracking, enhancing the purity and commercial value of oil and gas resources.The paper also highlights the existing issues and challenges, including optimizing preparation processes, reducing the production costs of cellulose nanomaterials, improving the environmental friendliness of the preparation process, enhancing the temperature and salt resistance of cellulose nanomaterials to meet the requirements of ultra-deep and special deep applications, developing technologies for controllable recovery and recycling of cellulose nanomaterials, evaluating their potential environmental impacts, and suggesting close collaboration between universities and petroleum-related enterprises for rapid technology transfer and widespread application.
Led by Academician Sun Jinsheng, the drilling fluid research team has been closely focusing on China's significant demands for ultra-deep and special deep oil and gas, unconventional oil and gas, and hydrate resources. They have conducted a series of research in drilling fluid technology, wellbore stability technology, reservoir protection technology, leak prevention and plugging technology, and have undertaken over 10 projects including national natural science foundation basic science center projects/major projects/key projects, national key research and development programs, major projects of CNPC and Sinopec, and have received more than 11 awards at the provincial and ministerial levels. Several teachers have been selected as national-level young talents, providing essential support for the efficient drilling and production of ultra-deep and special deep oil and gas resources in China.
|
PROGRAMS Undergraduates Master Doctoral Postdocs |
RESEARCH Drilling Production Reservoir Oilfield Chemistry Offshore O&G Ocean Engineering |
INTERNATIONAL International students Study abroad International Joint Lab International Visits |
CONTACTS US
|